How to combine ARExample and URP
- Author: Enox Software
- Category: Tips
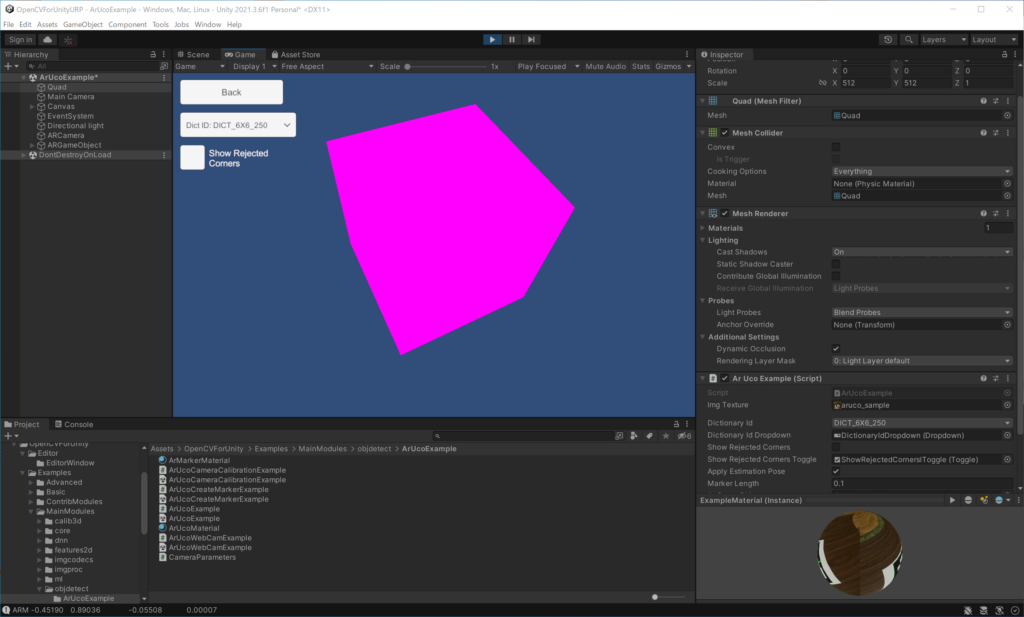
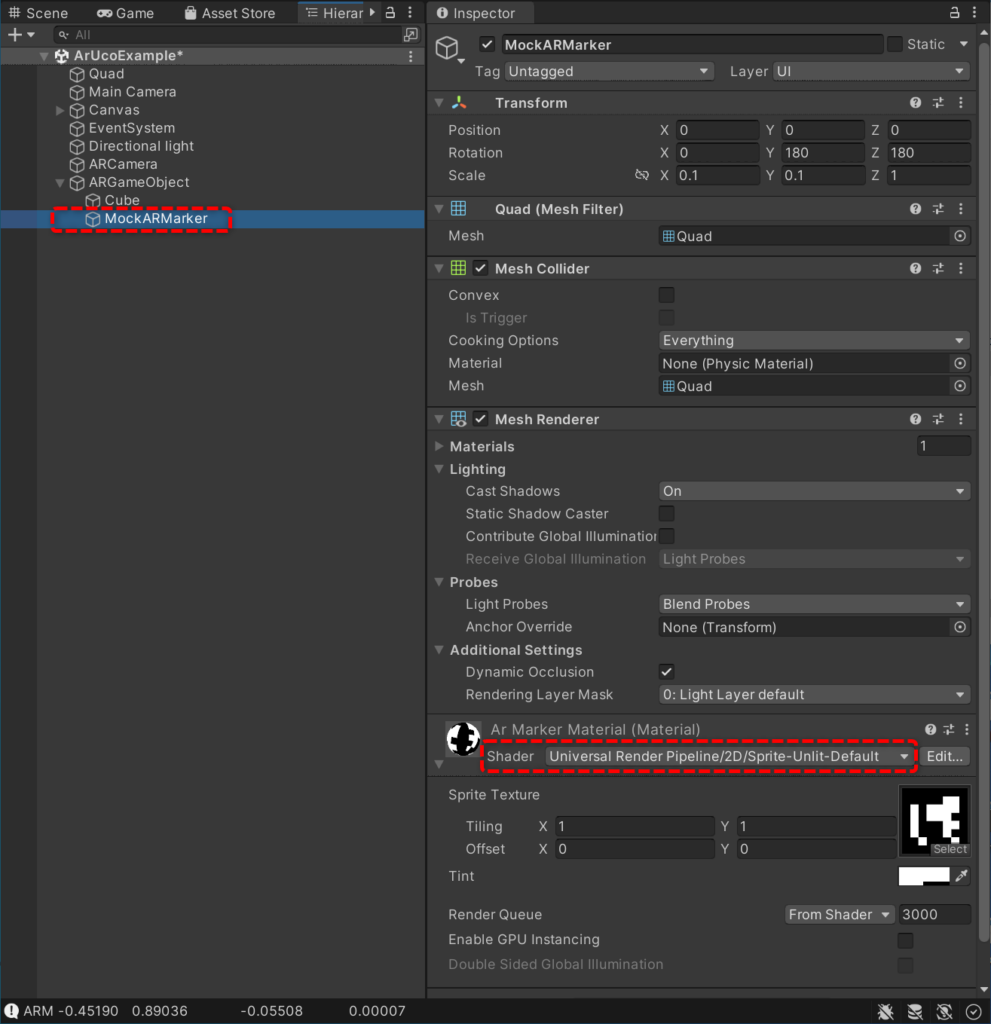
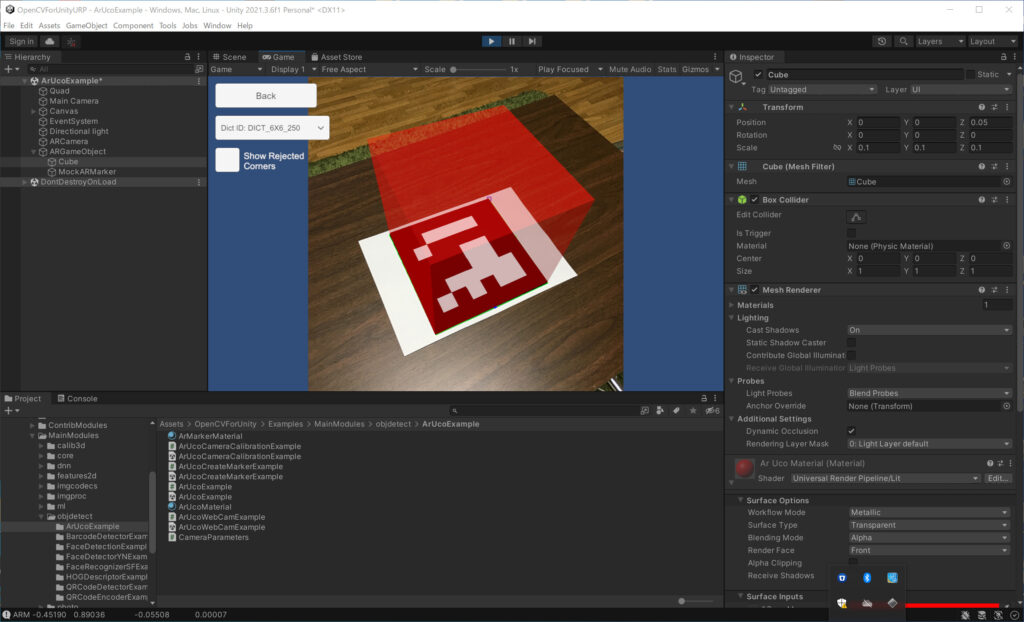
The Universal Render Pipeline (URP) is a prebuilt Scriptable Render Pipeline, made by Unity. OpenCVforUnity itself works fine with any render pipeline, but the ARExample, which superimposes two camera images, does not render well in the URP project. This is because some components of the ARExample are configured for the built-in rendering pipeline. By setting these settings for the universal rendering pipeline, AR objects will render correctly.
- MainCamera
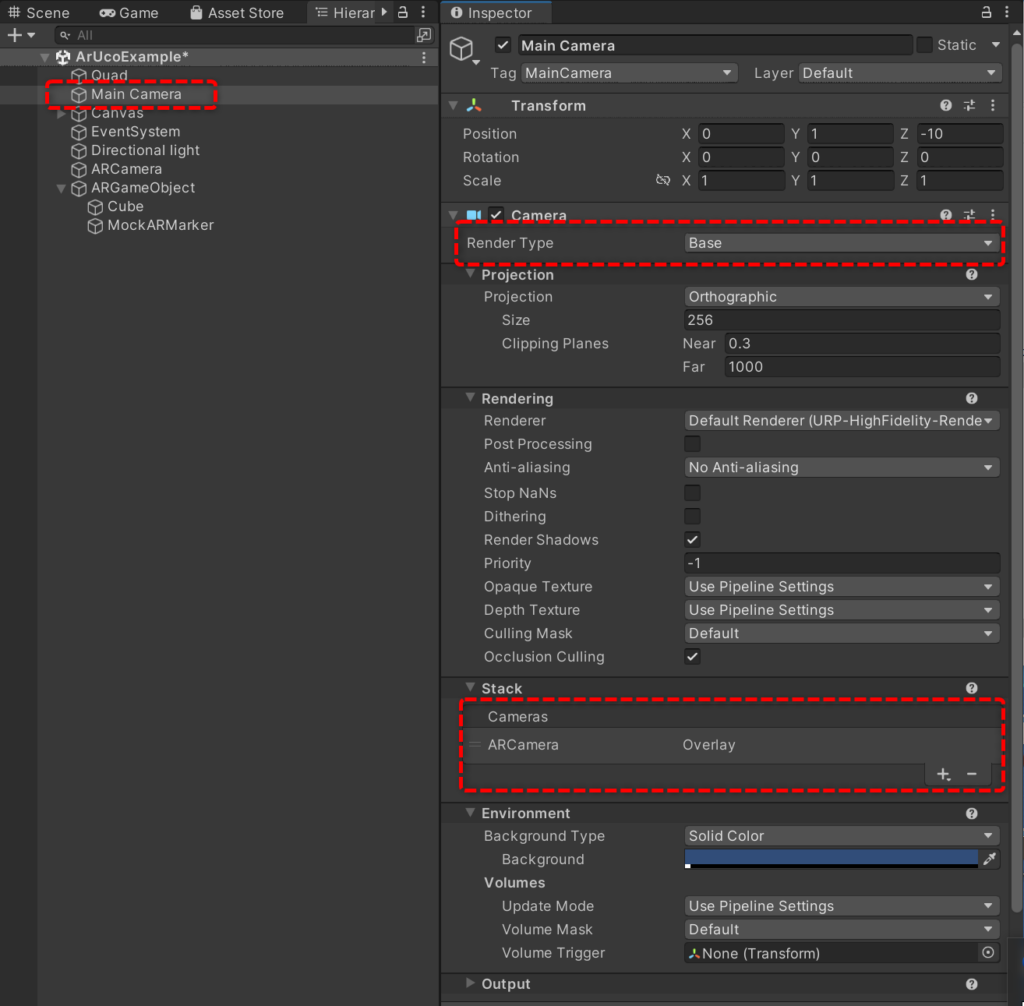
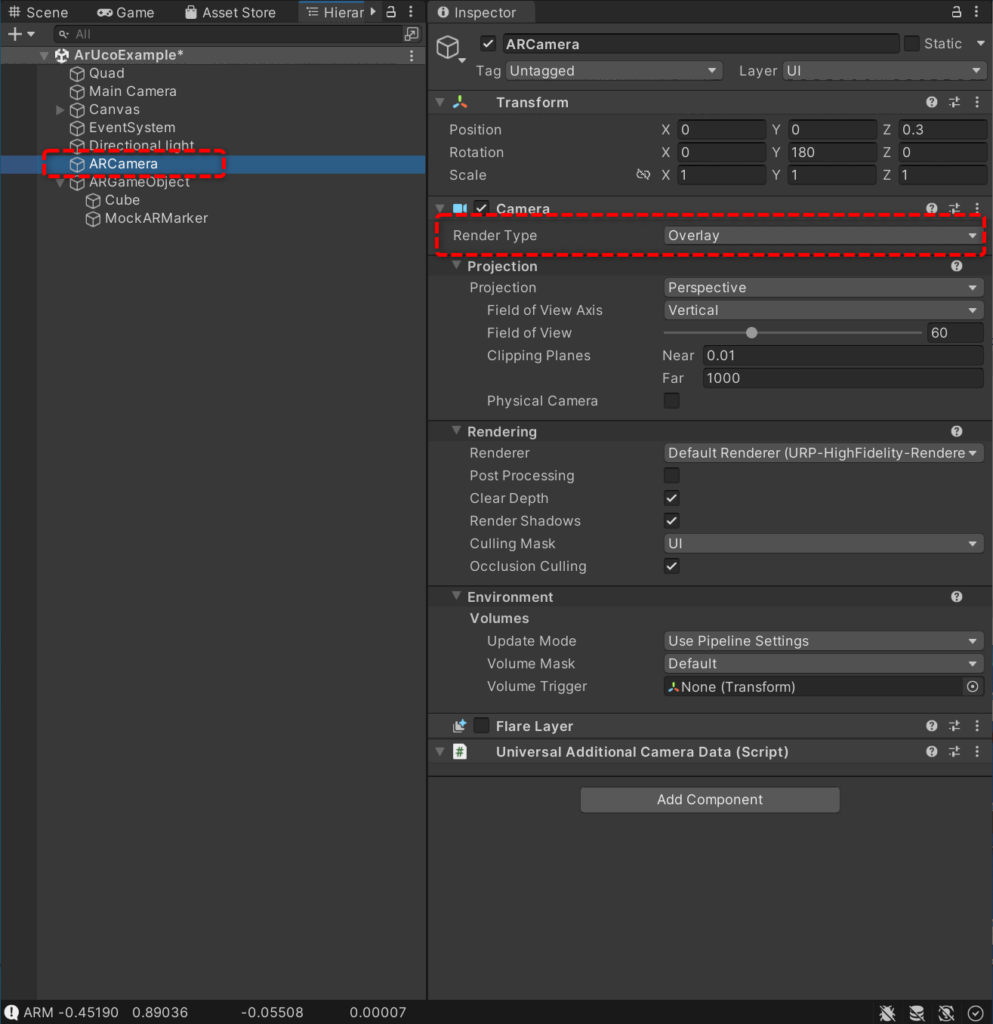
- ARCamera
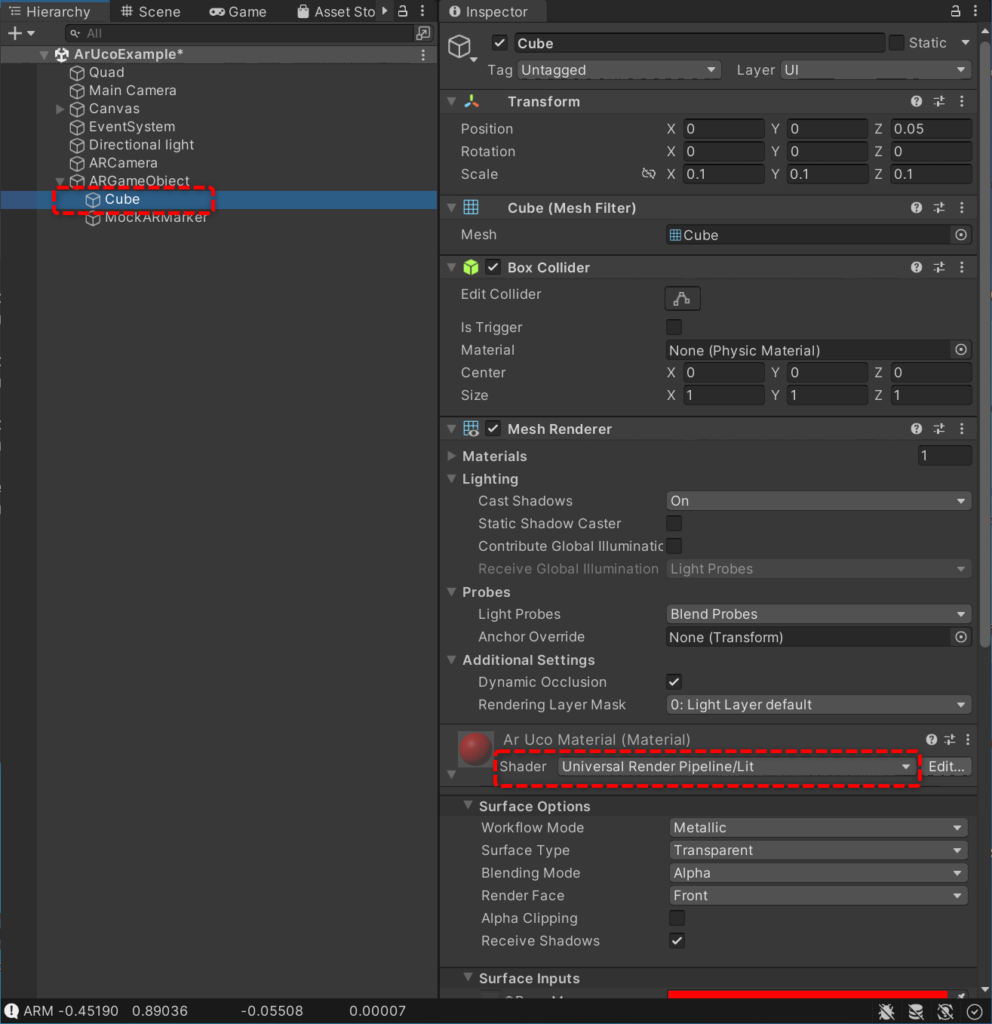
- Cube
- MockARMarker
ScreenShot
Related posts
Way to translation of Mat class operators defined in C++
This is a list of implemented matrix operations that can be combined in arbitrary complex expressions (here A, B stand for matrices ( Mat ), s for a scalar ( Scalar ), alpha for a real-valued scalar ( double )): Note: In C++, the left-hand operand of compound assignment operators like “A += B” is reused, and operations such as “Core.add(A, B, A)” are performed internally. However, in C#, it is not possible to explicitly overload compound assignment operators. Instead, binary operator overloading is used implicitly, which results in a new Mat object being created and assigned to A each time an operator is used. This behavior leads to different memory management between C++ and C#. c++OpenCVForUnity(C#)Addition, subtraction, negation: A+B, A-B, A+s, A-s, s+A, s-A, -AA + BM1 + M2Core.add (M1, M2, M_dst)A – BM1 – M2Core.subtract (M1, M2, M_dst)A + sM1 + sCore.add (M1, s, M_dst)A – sM1 – sCore.subtract (M1, s, M_dst)-A-M1Core.multiply (M1, Scalar.all (-1), M_dst)Scaling: A*alpha A/alphaA * αM1 * 3Core.multiply (M1, Scalar.all (3), M_dst)A / αM1 / 3Core.divide (M1, Scalar.all (3), M_dst)Per-element multiplication and division: A.mul(B), A/B, alpha/AA.mul(B)M1.mul(M2)M1.mul (M2)A / BM1 / M2Core.divide (M1, M2, M_dst)α / A3 / M1Core.divide (new Mat (M1.size (), M1.type (), Scalar.all (3)), M1, M_dst)Matrix multiplication: A*BA * BM1 * M2Core.gemm (M1, M2, 1, new Mat (), 0, M_dst)Comparison: A cmpop B, A cmpop alpha, alpha cmpop A, where […]
- Author: Enox Software
- Category: Tips
Mat Basic Processing2
These codes are included in the OpenCVForUnity Example Unity scenes. (MatBasicProcessingExample) Merge Example Code: // // simple composition: Merge example // // 2×2 matrix Mat m1 = new Mat (2, 2, CvType.CV_64FC1); m1.put (0, 0, 1.0, 2.0, 3.0, 4.0); Mat m2 = new Mat (2, 2, CvType.CV_64FC1); m2.put (0, 0, 1.1, 2.1, 3.1, 4.1); Mat m3 = new Mat (2, 2, CvType.CV_64FC1); m3.put (0, 0, 1.2, 2.2, 3.2, 4.2); List<Mat> mv = new List<Mat>(); mv.Add (m1); mv.Add (m2); mv.Add (m3); // merge Mat m_merged = new Mat(); Core.merge (mv, m_merged); // dump Debug.Log (“”m_merged=”” + m_merged.dump()); Execution Result: m_merged=[1, 1.1, 1.2, 2, 2.1, 2.2; 3, 3.1, 3.2, 4, 4.1, 4.2] MixChannels Example Code: // // complex composition: mixChannels example // // 2×2 matrix Mat m1 = new Mat (2, 2, CvType.CV_64FC1); m1.put (0, 0, 1.0, 2.0, 3.0, 4.0); Mat m2 = new Mat (2, 2, CvType.CV_64FC1); m2.put (0, 0, 1.1, 2.1, 3.1, 4.1); Mat m3 = new Mat (2, 2, CvType.CV_64FC1); m3.put (0, 0, 1.2, 2.2, 3.2, 4.2); List<Mat> mv = new List<Mat>(); mv.Add (m1); mv.Add (m2); mv.Add (m3); // mat for output must be allocated. Mat m_mixed1 = new Mat(2, 2, CvType.CV_64FC2); Mat m_mixed2 = new Mat(2, 2, CvType.CV_64FC2); MatOfInt fromTo = new MatOfInt (0,0, 1,1, 1,3, 2,2); List<Mat> mixv = new List<Mat> (); mixv.Add (m_mixed1); mixv.Add (m_mixed2); // […]
- Author: Enox Software
- Category: Tips
How to catch native OpenCV’s errors code (CVException handling)
In order to display the native opencv’s error code, please enclose the code in Utils.setDebugMode(true) and Utils.setDebugMode(false). Example Code: // // CVException handling example // // 32F, channels=1, 3×3 Mat m1 = new Mat (3, 3, CvType.CV_32FC1); m1.put (0, 0, 1.0f, 2.0f, 3.0f, 4.0f, 5.0f, 6.0f, 7.0f, 8.0f, 9.0f); // 8U, channels=1, 3×3 Mat m2 = new Mat (3, 3, CvType.CV_8UC1); m2.put (0, 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9); // dump Debug.Log (“”m1=”” + m1); Debug.Log (“”m1.dump()=”” + m1.dump ()); Debug.Log (“”m2=”” + m2); Debug.Log (“”m2.dump()=”” + m2.dump ()); #if UNITY_STANDALONE || UNITY_EDITOR // Publish CVException to Debug.LogError. Utils.setDebugMode (true, false); Mat m3 = m1 / m2; Utils.setDebugMode (false); // Throw CVException. Utils.setDebugMode (true, true); try { Mat m4 = m1 / m2; } catch (Exception e) { Debug.Log (“”CVException: “” + e); } Utils.setDebugMode (false); #else Debug.Log (“”The setDebugMode method is only supported on WIN, MAC and LINUX.””); #endif Execution Result: m1=Mat [ 3*3*CV_32FC1, isCont=True, isSubmat=False, nativeObj=0x820637680, dataAddr=0x820295296 ] m1.dump()=[1, 2, 3; 4, 5, 6; 7, 8, 9] m2=Mat [ 3*3*CV_8UC1, isCont=True, isSubmat=False, nativeObj=0x820637792, dataAddr=0x820619712 ] m2.dump()=[ 1, 2, 3; 4, 5, 6; 7, 8, 9] core::divide_12() : OpenCV(3.4.1-dev) C:\Users\xxxxx\Desktop\opencv\modules\core\src\arithm.cpp:683: error: (-5) When the input arrays in add/subtract/multiply/divide functions have different types, the output array type must be explicitly specified in function cv::arithm_op m3=Mat [ […]
- Author: Enox Software
- Category: Tips

